Imagine someone going through your important papers and files without your permission. That’s what a data breach is like, but in the digital world. It happens when sensitive information, like passwords, credit card details, or even health records, is accessed by someone who shouldn’t have it.
Data breaches are a big problem in Australia, and they can happen to businesses of any size. The more information businesses store online, the more important it is to understand how to protect themselves.
This guide will explain what data breaches are, what can happen if one occurs, and some easy steps businesses can take to keep their information safe.

What is a Data Breach?
A data breach is when private information is accessed by someone who isn’t authorised to see it.
This can happen in a few different ways, like:
- Tricking people into giving up their information: This is called phishing, and it’s when scammers send emails or messages that look like they’re from a real company. The emails or messages will try to trick you into clicking on a link or opening an attachment that will steal your information.
- Hacking into computer systems: Hackers are like digital thieves who break into computer systems to steal information. They can use special programs to find weaknesses in computer security and then exploit them to get access to sensitive information.
- Losing devices that store information: If a laptop, phone, or USB drive that has sensitive information on it is lost or stolen, it could lead to a data breach.
What is a Data Breach in Cyber Security?
A data breach in cybersecurity is simply a more specific way of saying “data breach.” A data breach always involves a security issue, so the two terms mean the same thing.
Notifiable Data Breaches in Australia:
Imagine you run a shop and you have a list of your customers’ names, addresses, and phone numbers. A notifiable data breach happens when someone steals this list without your permission, and it could cause serious trouble for your customers.
Difference Between Regular Data Breach and Notifiable Data Breach
Not every time someone tries to break into your computer system is a notifiable data breach. It only becomes one if stealing the information could cause serious problems for your customers. For example, if someone steals your customers’ credit card numbers, that’s a big problem and is a notifiable data breach.
When and Where to Tell the Government
If you think your customers’ information has been stolen and it could cause them serious problems, you need to tell the Australian government. You should tell the Office of the Australian Information Commissioner (OAIC). You usually have to tell them within 30 days of finding out about the data breach.
What Happens If You Don’t Tell the Government
If you don’t tell the government about a notifiable data breach, you could get into trouble. It’s important to be honest and open about what happened. The government can help you and your customers deal with the problem.
Remember: It’s always better to be safe than sorry. If you’re unsure if something is a notifiable data breach, it’s better to contact local cyber security provider or the OAIC for advice.
Types of Data Breaches
There are many ways hackers can steal your business’s important information. Understanding these helps you protect your business.
Common Types of Data Breaches
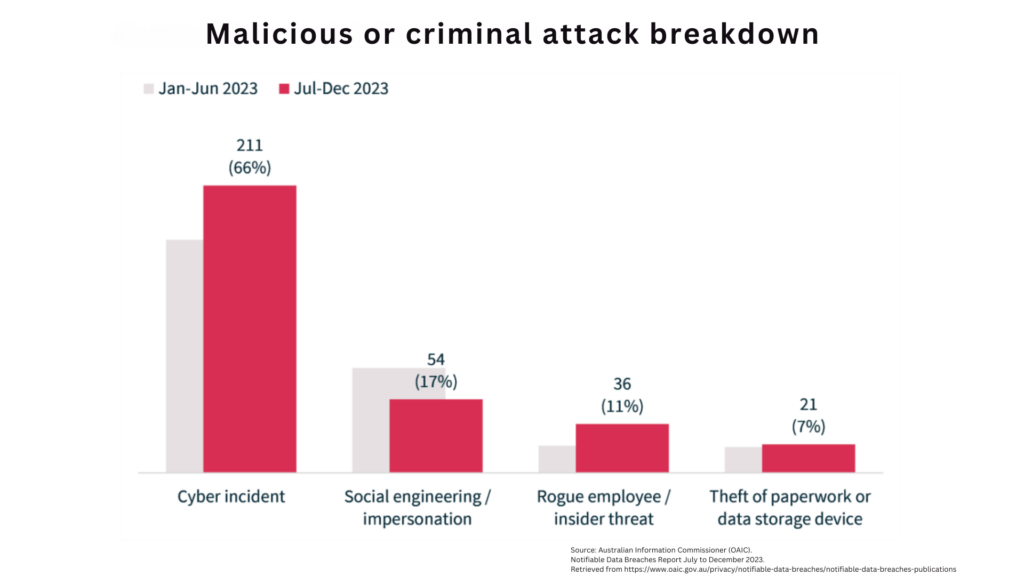
- Hacking: This is when someone breaks into your computer system without permission.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Hackers pretend to be someone else to fool people into giving away their information.
- Malware: Bad software can sneak into your computers and steal information.
- Insider Threats: People who work for your business might steal information.
- Physical Theft: If someone loses or steals your computers or phones, your information could be at risk.
- Accidental Data Loss: Sometimes people accidentally share or delete important information.
Knowing about these threats helps businesses put strong security measures in place.
The Impact of Data Breaches
A data breach can cause big problems for Australian businesses, no matter how big or small they are. It’s important to understand what could happen so you can protect your business.
Financial Consequences
- Extra costs: You might have to pay for lawyers, investigators, and fixing the problem. You might also need to pay for checking people’s credit scores and government fines.
- Lost money: Your business might lose customers and sales because of the breach.
- Higher bills: Your insurance costs could go up after a data breach.
Reputational Damage
- Loss of customer trust: Customers might stop trusting your business to protect their information.
- Negative press: News about the data breach can spread quickly and hurt your business’s image.
- Impact on customer relationships: Customers may take their business elsewhere following a data breach.
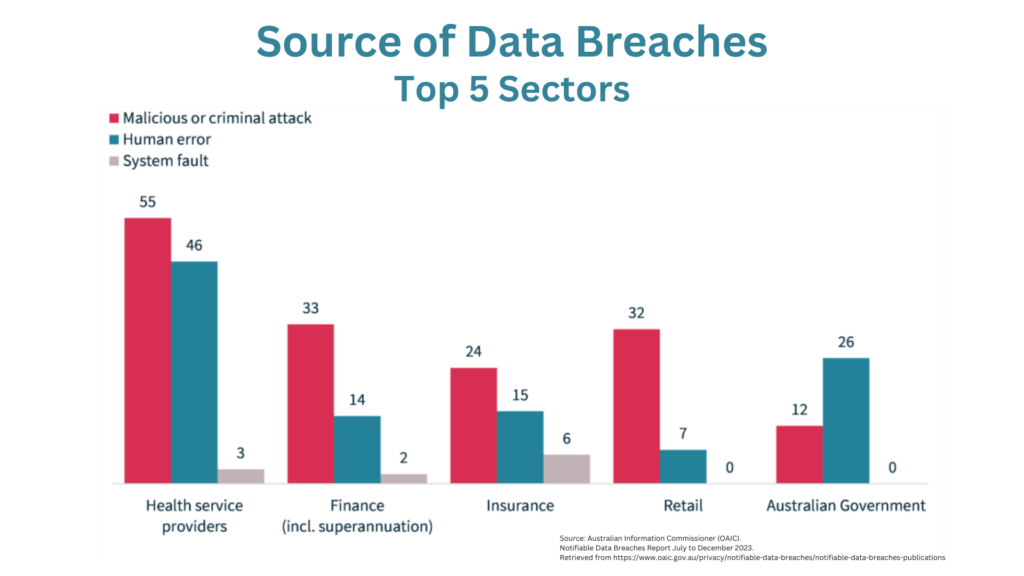
Operational Problems
- System downtime: When trying to fix the problem, your business might have to close down for a while.
- Reduced productivity: Your workers might spend time dealing with the mess instead of doing their jobs.
- Supply chain issues: Problems with data breaches can also affect the businesses you work with, which can cause problems for you.
Understanding these problems can help you see why it’s important to protect your business from data breaches.
How Data Breaches Happen
To stop hackers, it helps to understand how data breaches work. Even though hackers use tricky ways, most attacks follow a similar plan.
The Data Leakage Lifecycle
- Research: Hackers look for businesses to target. They learn about the business, its computers, and its employees.
- Attack: Cybercriminals try to break in using different methods like phishing emails, harmful software, or finding weaknesses in the computer system.
- Stealing Information: Once access is gained, attackers steal sensitive information and transfer it to their control.
Common Causes of Data Breaches:
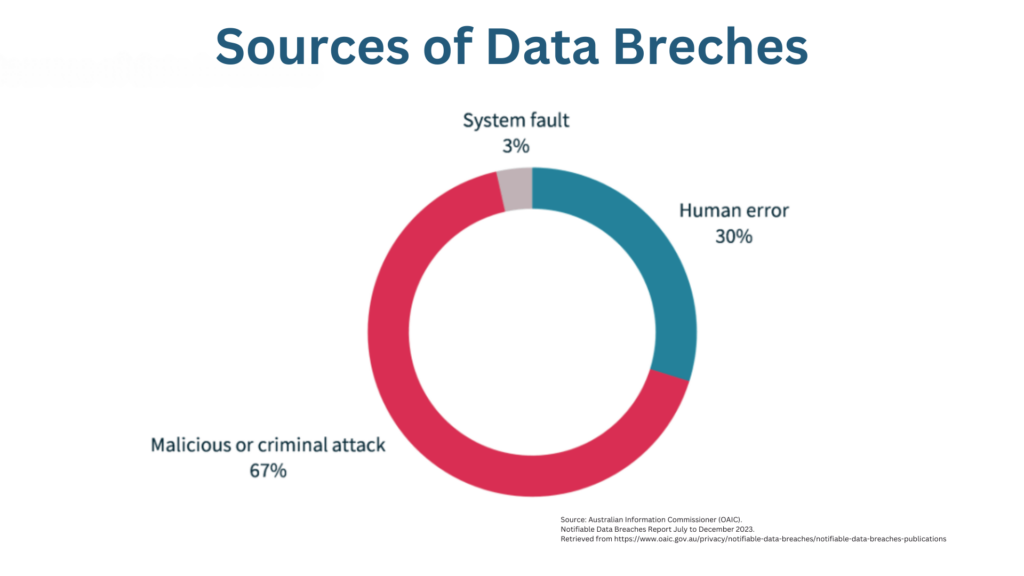
Data breaches often happen due to a few key issues:
- Human error: Mistakes by employees, like clicking on suspicious links or mishandling sensitive information, can lead to breaches.
- Weak security: Poor passwords, outdated software, or insufficient network protection can leave businesses vulnerable.
- Cyberattacks: Hackers exploit vulnerabilities in systems to steal data.
- Insider threats: Employees or contractors with access to sensitive information might misuse it.
- Physical security failures: Lost or stolen devices containing sensitive data can compromise information.
Understanding these common causes is essential for building strong data protection measures.
Preventing Data Breaches
Protecting your Australian business from data breaches starts with a solid data protection plan. By combining the right technology with proper employee training, you can significantly lower the chances of a breach.
Key Prevention Strategies
- Employee Training and Awareness: Training your employees on data security is vital. They need to know how to spot phishing scams, create strong passwords, and understand why keeping data confidential is crucial. Regular training sessions and phishing drills can help reinforce these practices.
- Strong Password Policies and Multi-Factor Authentication: Make sure employees use strong, complex passwords and change them regularly. Adding multi-factor authentication (MFA) provides extra security by requiring multiple verification steps before accessing systems.
- Data Encryption: Protect sensitive information by encrypting it both at rest (when stored) and in transit (when transferred). This makes it much harder for unauthorised people to access the information.
- Access Controls: Limit who can access sensitive data by enforcing strict access controls. Use the principle of least privilege, meaning employees only have access to the information they need for their jobs. Regularly review and update access permissions to ensure they align with current roles and responsibilities.
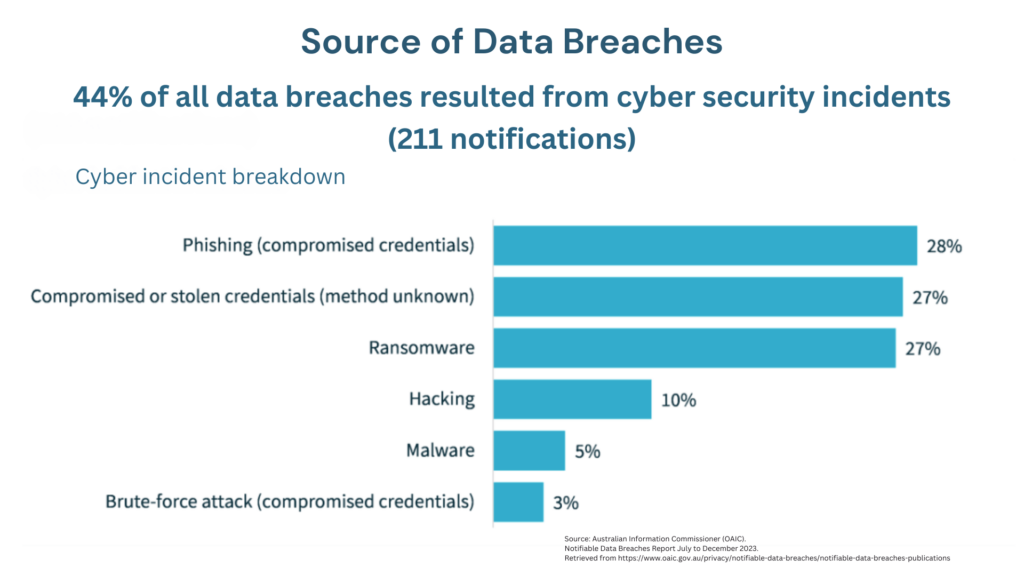
- Regular Security Audits and Assessments: Conduct regular security audits to find and fix any weaknesses in your systems and networks. You might consider hiring an external cybersecurity expert for a thorough assessment.
- Network Security: Protect your network with firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security measures. Make sure all software and systems are kept up-to-date with the latest patches and security updates.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a detailed plan for responding to a data leakage. This should include steps to contain the breach, notify affected parties, and restore normal operations.
- Data Minimisation and Retention: Only collect and keep personal information that’s necessary for your business. Regularly review and delete data that’s no longer needed.
- Privacy by Design: When designing new systems and processes, make sure privacy is a key consideration from the start.
The Cost of a Data Breach
The financial impact of a data breach can be severe for Australian businesses, no matter their size. Beyond the immediate costs of handling the incident, the long-term effects can be extensive.
According to the IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average total cost of a data breach surged from USD 3.92 million in 2019 to USD 4.88 million in 2024, representing a 24.5% increase over the past five years.
Financial Implications
- Direct Costs: These include legal fees, forensic investigations, public relations efforts, credit monitoring for those affected, and regulatory fines from the Australian Information Commissioner.
- Loss of Revenue: A data leakage can harm a company’s reputation, leading to reduced sales, customer turnover, and missed business opportunities.
- Increased Insurance Premiums: Following a data breach, insurance premiums may rise significantly.
Hidden Costs
- Decreased Productivity: Employees may spend time managing the fallout from a breach, which can lower overall productivity.
- Customer Acquisition Costs: Rebuilding trust with customers after a data breach can be both costly and time-consuming.
- Long-Term Reputational Damage: The negative impact of a data breach can linger for years, making it harder for the company to attract customers and partners.
Understanding the true cost of a data breach helps you understand why you need strong security. By figuring out how much a data leakage could cost your business, you can make smart choices about protecting yourself.
Essential Eight can significantly help prevent data breaches.
The Essential Eight is a set of cybersecurity measures developed by the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) to protect businesses from cyberattacks.
These measures are designed to make it much harder for hackers to steal your information.
By following the Essential Eight, you’re taking important steps to protect your business from common threats like:
- Phishing attacks
- Malware infections
- Unauthorised access
While it’s not a guarantee against all cyber threats, the Essential Eight provides a strong foundation for protecting your business
Conclusion
Data breaches are a big problem for Australian businesses. Hackers are always trying new ways to steal information. That’s why it’s important to protect your business and your customers.
Netcomp is here to help. We’re experts in keeping businesses safe from hackers. We can help you understand the risks, protect your information, and recover if something bad happens. Don’t wait until it’s too late. Protect your business today. Contact Netcomp for expert advice and support.



