Imagine losing all your customer data, financial records, and operational files in an instant. Indeed, this is the stark reality of a cyberattack for a growing number of Australian small businesses. Consequently, understanding and implementing robust computer network security is no longer optional but rather a fundamental necessity for survival in today’s digital landscape. Furthermore, the increasing prevalence of cyberattacks specifically targeting small businesses across Australia underscores this critical need. For example, data breaches can have a devastating impact on a business’s reputation, leading to a loss of customer trust and significant financial consequences. Moreover, the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) actively provides resources and guidance, and relevant regulations. For example Privacy Act further emphasise the importance of protecting sensitive information. In fact, the financial impacts of cyberattacks on Australian small businesses can be significant, covering recovery costs, legal fees, and potential fines.
Therefore, this article will delve into the essentials of computer network security. Firstly, we will clearly define what network security includes and explore its core elements. Secondly, we will break down the different types of network security measures that Australian businesses should be aware of. Finally, we will touch upon practical security measures and the constantly evolving threat landscape, providing a foundational understanding for protecting your digital assets.

Defining Computer Network Security
In simple terms, computer network security means keeping your computer network, the information stored on it, and the computers and devices connected to it safe from people who shouldn’t have access. Essentially, it’s about protecting your digital world from being seen, used, changed, or destroyed by unauthorised individuals.
How Does Network Security Actually Work?
Fundamentally, network security operates based on a few key ideas working together:
- Verifying Who You Are (Authentication). Firstly, when you try to access a network, the system needs to confirm that you are who you say you are. For instance, this is similar to showing your driver’s license to prove your identity.
- Giving Permission (Authorization). Secondly, once your identity is confirmed, the system checks what you are allowed to do on the network. For example, an employee in the sales department might have access to customer records, whereas an employee in accounting might not.
- Secret Codes (Encryption). Moreover, to keep information safe as it travels across the internet or is stored on computers, it’s often scrambled into a secret code. Consequently, this process, called encryption, makes the data unreadable to anyone who doesn’t have the correct “key” to unlock it.
- Digital Gatekeepers (Firewalls). Additionally, imagine a firewall as a security guard for your computer network. Indeed, it carefully watches all the traffic trying to enter or leave your network and blocks anything that looks suspicious or harmful.
- Silent Watchdogs (Intrusion Detection Systems). Besides firewalls, there are also systems that quietly monitor all the activity on your network, constantly looking for any signs of someone trying to break in or do something they shouldn’t. Therefore, these are called intrusion detection systems.
The Ever-Changing Threats
However, it’s important to remember that the dangers online are constantly changing. For example, cybercriminals are always coming up with new and clever ways to try and get past security measures. Thus, it’s crucial for Australian businesses to have a strong and adaptable approach to network security to stay protected from these evolving threats.
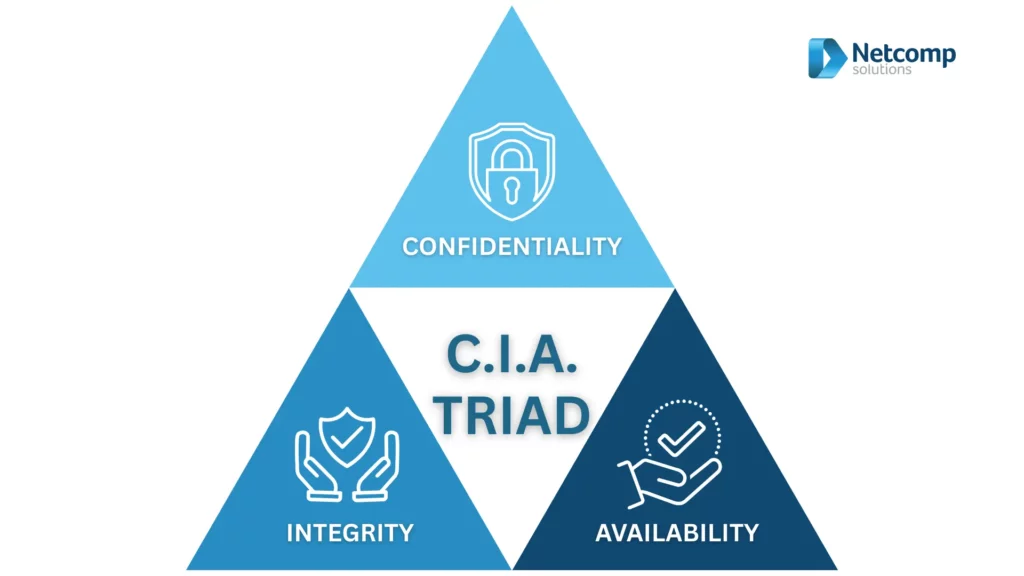
The Core Elements of Network Security (The CIA Triad)
Essentially, strong network security is built upon three fundamental principles, often referred to as the CIA triad: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. Consequently, understanding each of these elements is crucial for any Australian business looking to protect its digital assets.
1. Confidentiality: Keeping Secrets Safe:
Firstly, confidentiality is all about making sure that sensitive information can only be accessed by people who have permission. In other words, it’s about protecting your business’s secrets from falling into the wrong hands. For instance, imagine your customer database or financial records; clearly, you wouldn’t want unauthorised individuals viewing or copying this information. To achieve this, several techniques are used.
- For example, encryption scrambles data so that it’s unreadable to anyone without the correct decryption key.
- Furthermore, access controls, such as passwords and user permissions, ensure that only authorised users can log in and view specific files or systems.
- Moreover, data masking is another technique where sensitive data is hidden or replaced with fake information for non-essential users, like showing only the last few digits of a credit card number.
2. Integrity: Ensuring Accuracy and Trust
Secondly, integrity focuses on maintaining the accuracy and consistency of your data. That is to say, it’s about making sure that your information hasn’t been tampered with, either accidentally or maliciously. For example, you need to be confident that the sales figures in your reports are accurate and haven’t been altered.
To ensure data integrity, various methods are employed.
- For instance, hashing creates a unique digital fingerprint of data. If the data is changed, the fingerprint will also change, alerting you to potential tampering.
- Additionally, digital signatures can verify the authenticity of a document and confirm that it hasn’t been altered since it was signed.
- Furthermore, version control systems track changes made to files over time, allowing you to revert to previous, untainted versions if necessary.
3. Availability: Always Being There When You Need It
Thirdly, availability ensures that your network resources and data are accessible to authorised users whenever they need them. In other words, even if there’s a technical issue or an attack, your essential systems should remain operational. For example, if your website goes down, customers won’t be able to access your services, potentially leading to lost revenue and reputational damage.
To ensure high availability, several strategies are implemented.
- For instance, redundancy involves having backup systems and hardware in place. So if one component fails, another can immediately take over.
- Moreover, regular backups of your data ensure that you can restore your information in case of data loss due to hardware failure, cyberattacks, or natural disasters.
- Finally, comprehensive disaster recovery plans outline the steps your business will take to restore its IT infrastructure and operations quickly after a disruptive event.
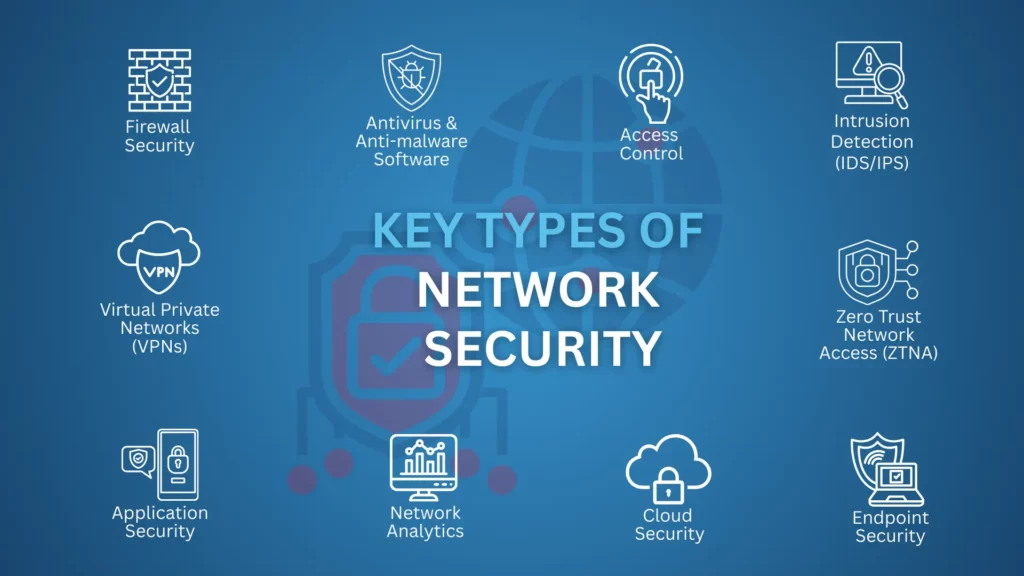
The 10 Key Types of Network Security
To effectively protect their digital environments, Australian businesses need to understand and implement various types of network security measures. Consequently, here are ten key types that play a crucial role in building a robust security posture:
1. Firewall Security
Firstly, firewalls act as gatekeepers for your computer network security, carefully watching all the data traffic that tries to enter or leave. Essentially, they examine this traffic and block anything that doesn’t meet pre-defined security rules.
For example, you can think of a firewall as a security guard at the entrance of your digital building, only allowing authorised traffic to pass.
Furthermore, there are different types of firewalls available.
- For instance, hardware firewalls are physical devices that sit between your network and the internet.
- Alternatively, software firewalls are programs installed on individual computers or servers.
- Moreover, cloud-based firewalls are services hosted in the cloud, offering scalable protection for cloud-based infrastructure and applications.
2. Access Control
Secondly, access control focuses on limiting who can access your network and what they can do once they’re in. Specifically, this involves setting up rules and permissions to ensure that only authorised individuals can view or modify sensitive information.
For example, access control lists (ACLs) are like lists of rules that specify which users or devices are allowed to access certain parts of the network.
Additionally, role-based access control (RBAC) assigns access rights based on a user’s role within the organisation, making it easier to manage permissions for groups of users.
Moreover, it’s crucial to enforce strong security practices like using strong passwords that are difficult to guess and implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) . Which requires users to provide two or more forms of identification (like a password and a code from their phone) before granting access.
3. Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
Thirdly, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) work like sophisticated alarm systems for your network. Indeed, they continuously monitor network traffic for any suspicious activity or known attack patterns. Furthermore, while an IDS primarily detects and alerts you to potential threats, an IPS goes a step further by automatically taking action to block or contain those threats. Consequently, these systems are vital for identifying and neutralising malicious activity before it can cause significant damage.
4. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
Fourthly, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) create secure, encrypted connections over a public network like the internet. Essentially, they establish a private “tunnel” for your data, protecting it from eavesdropping as it travels. For instance, VPNs are particularly important for remote workers who need to securely access the company network from home or while travelling. Similarly, they are also valuable for connecting branch offices securely, as if they were on the same local network.
5. Antivirus and Anti-malware Software
Fifthly, antivirus and anti-malware software are essential tools for protecting individual computers and servers from malicious software. Specifically, this includes viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and spyware. Moreover, these programs work by scanning files and system activity for known threats and either removing or quarantining them. Therefore, it’s absolutely crucial to keep your antivirus and anti-malware software updated regularly, as new threats emerge constantly.
6. Application Security
Sixthly, application security focuses on protecting the software applications your business uses from security vulnerabilities. That is to say, weaknesses in applications can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorised access to your systems and data. Consequently, secure coding practices, which involve writing code with security in mind, are essential. Furthermore, regular application updates and patching are also critical to address any newly discovered vulnerabilities.
7. Endpoint Security
Seventhly, endpoint security is about securing all the individual devices that connect to your network, such as laptops, desktops, smartphones, and tablets. Indeed, these endpoints can be entry points for cyberattacks if they are not properly protected. Moreover, this includes implementing security measures on these devices, such as antivirus software, firewalls, and password policies. Additionally, mobile device security is an increasingly important aspect of endpoint security, given the prevalence of employees using their personal devices for work.
8. Cloud Security
Eighthly, with more Australian businesses adopting cloud computing, cloud security has become paramount. Specifically, cloud environments present unique security challenges compared to traditional on-premises networks. Consequently, implementing cloud firewalls and adhering to security best practices provided by your cloud service provider are essential for protecting your data and applications in the cloud.
9. Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Ninthly, Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a modern security model based on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Essentially, instead of assuming that users or devices inside the network are trustworthy, ZTNA requires strict verification for every user and device trying to access network resources, regardless of their location. Therefore, this approach significantly improves security by limiting the potential damage if an attacker manages to breach the initial perimeter.
10. Network Analytics
Finally, network analytics involves collecting and analysing network traffic data to identify patterns and anomalies that might indicate a security threat. Consequently, by monitoring network behaviour, businesses can detect unusual activity, such as large data transfers or connections to suspicious IP addresses, and respond proactively to potential attacks. Therefore, network analytics provides valuable insights for improving overall computer network security and incident response capabilities.
Putting It All Together
To truly understand the importance of computer network security, let’s look at a real-world example. Furthermore, we’ll then outline practical steps that Australian small businesses can take to secure their own computer networks.
A Real-World Network Security Example
Consider a small retail business right here in Gold Coast. For instance, they process numerous customer payments daily through their point-of-sale system and online store. Consequently, protecting this sensitive customer payment information is absolutely critical. To achieve this, they implement several key network security measures:
- Firstly, they install a firewall to control who can access their network and block malicious traffic.
- Secondly, they enforce strong password policies, requiring employees to use complex passwords and change them regularly.
- Moreover, they enable multi-factor authentication for all employee accounts, adding an extra layer of security beyond just a password.
- Additionally, they perform regular data backups of their sales data and customer information, ensuring they can recover quickly in case of a cyber incident or system failure.
Therefore, by implementing these measures, the business significantly reduces its risk of falling victim to cyberattacks and protects its valuable customer data and reputation.
Practical Steps for Computer Network Security (For Australian Small Businesses)
So, what actions can your l business take to bolster its network security? Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1.Know Your Weak Spots: Risk Assessment.
Firstly, it’s essential to conduct a thorough network security audit to identify any vulnerabilities in your current setup. Consequently, this will help you understand where your weaknesses lie and prioritise your security efforts.
2.Understanding the Threats.

Secondly, it’s important to be aware of the common dangers lurking online. For example, malware is a broad term for malicious software, including viruses that attach to files, worms that can spread without human interaction. And Trojans that disguise themselves as legitimate software.
Furthermore, spyware secretly monitors your activity, while adware bombards you with unwanted advertisements.
Moreover, zero-day attacks exploit previously unknown vulnerabilities in software. Additionally, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks overwhelm your systems with traffic, making them unavailable.
Besides these, man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks involve attackers intercepting communication between two parties, while SQL injection targets databases, and cross-site scripting (XSS) exploits vulnerabilities in websites.
Finally, phishing and social engineering tactics manipulate individuals into revealing sensitive information.
3.Locking Your Digital Doors: Strong Passwords and MFA.
Thirdly, implement robust password policies that require employees to use strong, unique passwords and change them regularly. Moreover, enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts to add an extra layer of computer network security.
4.Keeping Everything Up-to-Date: Regular Software Updates.
Fourthly, ensure that your operating systems, applications, and security software are always up to date with the latest patches. Consequently, these updates often include critical security fixes that address known vulnerabilities.
5.Guarding Your Network Traffic: Firewalls and Intrusion Detection.
Fifthly, install and properly configure firewalls to control network traffic and implement Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) to monitor for and block suspicious activity.
6.Planning for the Worst: Data Backups and Recovery.
Sixthly, regularly back up your critical data to a secure, offsite location. Furthermore, develop and test a comprehensive disaster recovery plan to ensure you can restore your operations quickly in case of data loss.
7.Your Human Firewall: Employee Training.
Seventhly, educate your employees about cybersecurity best practices, including how to identify phishing emails, the importance of strong passwords, and safe browsing habits.
8.Securing Your Wireless Connections: Secure Wi-Fi.
Eighthly, ensure that your Wi-Fi networks are secured with strong, unique passwords and the latest encryption protocols, such as WPA3.
9.Protecting Your Devices: Endpoint Protection.
Ninthly, implement antivirus and anti-malware software on all devices that connect to your network, including computers, laptops, and mobile devices.
10.Limiting the Damage: Network Segmentation.
Tenthly, divide your network into smaller, isolated segments. Consequently, this can help to contain a security breach and limit its impact on other parts of your network.
11.Staying Vigilant: Regular Security Audits.
Eleventhly, conduct periodic security audits to identify and address any new vulnerabilities that may have emerged.
12.Keeping Communications Private: Cryptography and Secure Protocols.
Twelfthly, understand the importance of encryption for protecting sensitive data in transit and at rest. Furthermore, ensure you are using secure communication protocols like HTTPS for your website and email.
13.Securing Your Remote Workforce: Remote Work Security.
Thirteenthly, if you have remote workers, ensure they are using VPNs to connect securely to your network. Additionally, enforce strong authentication and security policies for their devices.
14.Staying Operational: Business Continuity.
Finally, develop a comprehensive business continuity plan that outlines how your business will continue to operate in the event of a significant disruption, including cyberattacks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, remember that computer network security is not a one-time fix but an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, adaptation, and vigilance. As the threat landscape evolves, so too must your security measures.
Is your Brisbane or Gold Coast business looking for expert guidance and support in navigating the complexities of computer network security? For over 20 years, Netcomp Solutions has been a trusted partner for local businesses, providing professional advice and comprehensive business cybersecurity services tailored to your specific needs. Don’t leave your digital assets vulnerable. Contact Netcomp today for a consultation and take the first step towards a more secure future for your business.
We’re here to help you protect what matters most.



