Australian businesses face a cyber attack every six minutes. Moreover, data breaches now cost businesses an average of $4.88 million per incident globally. Consequently, traditional security methods simply aren’t enough anymore.
Zero trust security offers a revolutionary approach to protecting your business. Furthermore, this modern framework assumes no one is trustworthy by default—not even your own employees.

What Is Zero Trust Security?
Zero trust is a cybersecurity model built on one critical principle: “never trust, always verify.” Additionally, this approach treats every access request as a potential threat.
Traditional security operates like a castle with strong outer walls. However, once someone gets inside, they can access almost everything. In contrast, zero trust creates checkpoints throughout your entire network.
According to NIST Special Publication 800-207, zero trust assumes no implicit trust based on network location alone. Therefore, authentication happens continuously, not just at the network perimeter.
Why Australian Businesses Need Zero Trust Now
The Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) reports alarming statistics. Specifically, they responded to over 1,200 cyber security incidents in 2024-25. Furthermore, this represents an 11% increase from the previous year.
Between July and December 2024, the OAIC received 595 data breach notifications. Additionally, 2024 marked the highest notification count since reporting began in 2018.
Queensland and New South Wales businesses face particularly high risks. Moreover, small businesses often become prime targets because attackers perceive them as easier marks. Consequently, implementing robust security measures becomes absolutely critical.
Individuals in Australia now face an average $33,000 loss per cyber incident. Therefore, the financial impact extends beyond just large corporations.
Core Principles of Zero Trust Architecture
Never Trust, Always Verify
Zero trust eliminates automatic trust for anyone or anything. Instead, every user must prove their identity continuously. Additionally, this verification happens regardless of their location or previous access history.
The core philosophy treats all requests as potential threats, regardless of origin. Therefore, your finance manager accessing files from the office undergoes the same scrutiny as remote access.
Least Privilege Access
Users receive only the minimum access needed for their specific role. Furthermore, this principle significantly reduces potential damage from compromised accounts.
For example, your marketing team shouldn’t access financial records. Similarly, sales staff don’t require entry to technical infrastructure systems. Consequently, limiting access creates natural boundaries against threats.
Continuous Authentication and Monitoring
Traditional systems verify identity once at login. However, zero trust continuously validates users throughout their entire session.
The approach verifies each device, user, transaction, and data flow during the entire access process. Therefore, suspicious behaviour triggers immediate security responses.
Micro-Segmentation
Networks divide into small, isolated segments with separate access controls. Additionally, this prevents attackers from moving laterally across your systems.
A network using micro-segmentation may contain dozens of separate, secure zones. Consequently, breaching one area doesn’t grant access to everything else.
Assume Breach Mentality
Zero trust operates under the assumption that breaches will occur. Therefore, the framework focuses on minimising damage rather than just preventing entry.
This mindset drives organisations to implement multiple security layers. Furthermore, it ensures rapid detection and containment of threats.
Key Components of Zero Trust Implementation
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Strong identity verification forms the foundation of zero trust. Therefore, multi-factor authentication (MFA) becomes mandatory for all users.
Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures permissions align with job functions. Additionally, identity systems must integrate with all enterprise resources.
Device Security and Health Verification
Zero trust requires continuous validation of device posture, including checks for up-to-date operating systems and active firewalls. Furthermore, non-compliant devices face automatic quarantine until remediation occurs.
Your employees might use various devices for work. Therefore, each device undergoes security checks before accessing company resources.
Network Security and Segmentation
Traditional perimeter defences no longer suffice in distributed environments. Instead, zero trust protects individual resources regardless of network location.
Software-defined perimeters create secure access channels. Additionally, virtual private networks (VPNs) may integrate into zero trust frameworks.
Application and Workload Security
Applications require protection whether hosted on-premises or in cloud environments. Furthermore, zero trust principles apply to all software components.
API security becomes crucial for modern application architectures. Therefore, every interaction requires authentication and authorisation.
Data Security and Protection
Data represents your most valuable asset requiring protection. Additionally, encryption must cover data at rest and in transit.
Data loss prevention (DLP) tools monitor and control information movement. Furthermore, classification systems identify sensitive information automatically.
Benefits of Zero Trust for Australian SMBs
Enhanced Security Posture
Zero trust reduces the attack surface by enforcing least privilege access and continuous authentication. Consequently, unauthorised users cannot access sensitive data easily.
The framework provides multiple defence layers against sophisticated attacks. Therefore, even if one control fails, others remain active.
Reduced Data Breach Risk
Zero trust minimises data breach risk even if a device within the network becomes compromised. Additionally, micro-segmentation contains threats quickly.
Brisbane and Gold Coast businesses particularly benefit from this protection. Furthermore, reduced breach risk translates directly to lower financial exposure.
Improved Visibility and Control
Zero trust implementations provide comprehensive monitoring across all systems. Therefore, security teams can detect threats faster and respond more effectively.
Real-time analytics identify anomalous behaviour patterns immediately. Additionally, detailed logging supports forensic investigations after incidents.
Support for Remote Work
Australian businesses increasingly embrace flexible work arrangements. However, traditional security struggles with distributed workforces.
Zero trust enables secure access from anywhere, on any device. Furthermore, the framework maintains consistent security policies regardless of location.
Regulatory Compliance
The 2025 PSPF guidelines highlight the need for continuous improvement and a mindset that assumes breach. Therefore, zero trust helps meet evolving compliance requirements.
Australian regulations increasingly mandate stronger data protection measures. Additionally, zero trust provides frameworks that satisfy these obligations.
Cost Efficiency
While implementation requires investment, zero trust reduces long-term security costs. Furthermore, preventing breaches proves far cheaper than recovering from them.
Consolidated security platforms reduce complexity and operational expenses. Therefore, businesses can optimise their security spending effectively.
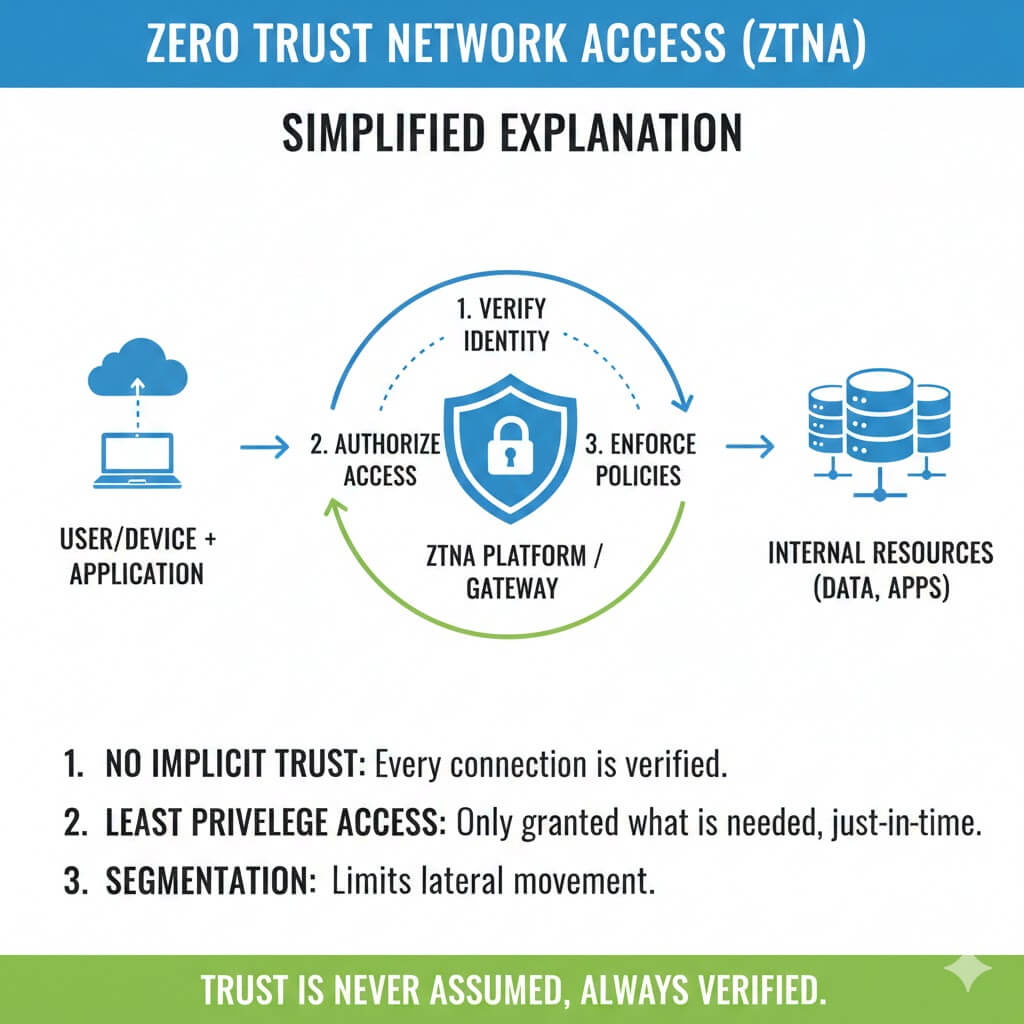
Implementing Zero Trust: Practical Steps for Australian Businesses
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning
Start by mapping all your data, applications, and users. Furthermore, identify your most critical assets requiring protection first.
Assess current security tools and identify gaps. Additionally, document all access pathways to sensitive resources.
Organisations should identify sensitive data and gain a deep understanding of where it’s stored, processed and transmitted. Therefore, comprehensive asset inventories become essential.
Phase 2: Identity and Access Controls
Implement multi-factor authentication across all systems immediately. Furthermore, this represents the fastest security improvement you can make.
Deploy single sign-on (SSO) to centralise access management. Additionally, establish clear role-based access policies for all users.
Phase 3: Device Management and Monitoring
Ensure all devices meet minimum security standards. Furthermore, deploy endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions.
Every user and device accessing the network requires continuous monitoring to ensure expected behaviour. Therefore, implement real-time monitoring tools immediately.
Phase 4: Network Segmentation
Divide your network into logical segments based on function. Furthermore, implement access controls between these segments.
Start with your most sensitive systems and data. Additionally, gradually extend segmentation across your entire infrastructure.
Phase 5: Continuous Monitoring
Deploy security information and event management (SIEM) systems. Furthermore, these tools aggregate logs from all sources.
Establish baseline behaviour patterns for users and systems. Additionally, configure alerts for anomalous activities.
Phase 6: Testing and Refinement
Regular security testing validates your zero trust implementation. Furthermore, penetration testing identifies remaining vulnerabilities.
Conduct quarterly reviews of access policies and permissions. Additionally, remove unnecessary access rights promptly.
Common Zero Trust Implementation Challenges
Legacy System Integration
Older systems may lack modern authentication capabilities. However, organisations can use gateways and proxies as intermediaries.
Gradual migration strategies allow phased zero trust adoption. Furthermore, prioritise high-risk systems for early implementation.
User Experience Concerns
Excessive security measures can frustrate legitimate users. Therefore, balance security with usability throughout implementation.
Modern MFA solutions offer seamless authentication experiences. Additionally, risk-based authentication reduces friction for low-risk activities.
Resource and Budget Constraints
Smaller organisations may struggle with budget or expertise. However, phased adoption allows manageable implementation timelines.
Start with high-risk assets to maximise risk reduction. Furthermore, managed service providers offer cost-effective implementation support.
Complexity and Integration
Multiple security tools must work together seamlessly. Therefore, choose solutions supporting open standards and interoperability.
Integrated platforms reduce complexity significantly. Additionally, consolidated management interfaces improve operational efficiency.
Zero Trust and Australian Compliance Requirements
Essential Eight Alignment
The ACSC‘s Essential Eight framework aligns well with zero trust principles. Furthermore, implementing zero trust helps achieve higher maturity levels.
Multi-factor authentication represents one Essential Eight control. Additionally, application control and patching complement zero trust approaches.
Privacy Act Obligations
Australian Privacy Principles require appropriate data security measures. Furthermore, zero trust provides robust frameworks for protecting personal information.
Continuous monitoring helps detect and respond to breaches quickly. Additionally, detailed logging supports mandatory breach notification requirements.
Industry-Specific Requirements
Financial services face additional APRA prudential standards. Furthermore, healthcare organisations must comply with state-based health records legislation.
Zero trust architectures support these various compliance frameworks. Additionally, the approach provides auditable security controls.
Choosing the Right Zero Trust Solution
Assess Your Business Needs
Consider your industry, size, and specific risk profile. Furthermore, identify your most critical assets requiring protection.
Evaluate your existing technology infrastructure and capabilities. Additionally, determine whether cloud-based or on-premises solutions suit you better.
Evaluate Vendor Solutions
Research vendors with proven Australian market experience. Furthermore, check their understanding of local compliance requirements.
Request demonstrations showing real-world implementation scenarios. Additionally, verify integration capabilities with your existing systems.
Consider Managed Services
Many Australian SMBs lack dedicated security expertise. Therefore, managed security service providers offer valuable support.
Brisbane and Gold Coast businesses can partner with local IT support providers. Furthermore, managed services provide ongoing monitoring and maintenance.
The Future of Zero Trust in Australia
The Australian government has pledged to develop a whole-of-government zero trust culture. Consequently, private sector adoption will likely accelerate significantly.
Cloud-native architectures increasingly incorporate zero trust principles by default. Furthermore, artificial intelligence will enhance automated threat detection capabilities.
Zero trust network access (ZTNA) will become standard components of enterprise architecture. Therefore, early adopters gain competitive security advantages.
Getting Started with Netcomp Solutions
Implementing zero trust doesn’t require massive upfront investment. Instead, start with foundational controls and build progressively.
Netcomp Solutions helps Brisbane and Gold Coast businesses implement practical zero trust strategies. Furthermore, our team understands Australian compliance requirements and local business challenges.
We provide comprehensive IT support and cyber security services tailored to SMBs. Additionally, our managed services ensure ongoing protection and monitoring.
Contact us today for a free security assessment. Furthermore, we’ll develop a customised zero trust roadmap for your business.
Our Zero Trust Services Include:
- Security Assessment: Comprehensive evaluation of current security posture
- Identity and Access Management: Implementation of MFA and SSO solutions
- Network Segmentation: Designing and deploying secure network architectures
- Endpoint Protection: Deploying and managing EDR solutions
- Security Monitoring: 24/7 monitoring and threat detection services
- Compliance Support: Ensuring adherence to Australian regulations
- Staff Training: Security awareness programs for your team
Key Takeaways
Zero trust represents the future of cyber security for Australian businesses. Furthermore, the framework addresses modern threats traditional security cannot stop.
Australian small businesses face increasing cyber threats daily. Therefore, implementing zero trust provides essential protection for your operations.
Start your zero trust journey today with manageable, phased implementation. Additionally, partner with experienced providers who understand local requirements.
The cost of prevention remains far lower than breach recovery expenses. Furthermore, zero trust protects your reputation, customer trust, and business continuity.
Don’t wait for a breach to take security seriously. Instead, implement zero trust principles now to safeguard your business future.
Ready to protect your business with zero trust security?
Contact Netcomp Solutions today:
- Phone: 1300 363 127
- Email: info@netcomp.com.au
- Website: www.netcomp.com.au
- Locations: Brisbane & Gold Coast, Queensland



