In today’s digital world, cyberattacks pose a significant threat to businesses of all sizes. Cyber attacks are on the rise, and businesses of all sizes are at risk. In 2022, the average cost of a data breach was $3.86 million, and that number is only going to go up. Just last year, cybercrime reports were coming in every 7 minutes on average, according to the latest annual cyber threat report by the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC).

Now, let’s demystify these cyber attacks. Think of them as sneaky tricks that these digital thieves use to get their hands on your valuable information. We’re talking about things like tricking your employees into giving away sensitive details or locking up your important data and demanding a ransom to unlock it. They might even send you seemingly harmless files that secretly cause chaos on your systems or overwhelm your website with so much traffic that it crashes.
But don’t worry, you don’t have to be an expert to defend your business. That’s where we step in. This article is your guide to understanding and dealing with cyberattacks. We’ll walk you through the different types of attacks in simple words and show you practical steps you can take to protect your digital fortress. Our goal is to provide you with the knowledge you need to safeguard your sensitive data and keep your business running smoothly. So, let’s dive in and arm you with the tools you need to outsmart those digital criminals!
What is a Cyberattack?
A cyber attack refers to any unauthorised attempt to gain access to computer systems, networks, or data with malicious intent. Cyber attacks aim to steal, change, disclose, disable, or destroy information, causing significant financial and reputational damage to businesses. These attacks can take many different forms and exploit vulnerabilities in technology and human behavior.
What are the 8 types of Cyberattacks?
Phishing Attacks
Phishing is one of the most common forms of cyber attacks. It involves tricking people into disclosing personal information, such as login credentials and credit card details, by impersonating a legitimate entity via email, messages, or websites.
Example: Imagine receiving an email that appears to be from your bank, requiring you to verify your account details urgently. You click on the link provided and unknowingly provide your sensitive information to hackers.
Malware Attacks

Malware, short for malicious software, refers to a class of harmful software designed to infiltrate and damage computer systems. It contains viruses, worms, and Trojans that can steal data, corrupt files, and disrupt operations.
Example: You download a seemingly harmless software update, that turns out to be a malware-infected file. This software secretly collects your personal information and sends it to cybercriminals.
Ransomware Attacks
It is a type of malware in which specific data or systems are kept hostage by attackers until a payment or ransom is paid. Ransomware attacks encrypt a victim’s data and demand a ransom payment in exchange for its release. This type of attack can paralyse a business’s operations and lead to significant financial losses.
Example: You open an attachment from an unknown sender, and suddenly, your computer’s files are encrypted. You receive a notification requesting payment in cryptocurrency in order to restore access to your data.
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
A DoS attack aims to overwhelm a network, server, or website with an excessive amount of traffic, rendering it unreachable to users. This can lead to downtime and financial losses.
Example: A website is flooded with an overwhelming amount of traffic, making it slow or completely inaccessible. This could be a competitor attempting to hurt your business by disrupting your online presence.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
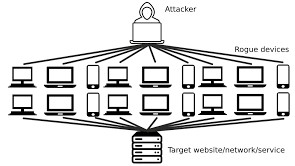
DDoS attacks are like a bigger, more coordinated version of DoS attacks. Instead of a single source flooding a target, DDoS assaults involve several sources, generally a network of hacked computers (a botnet), bombarding a target at the same time. This overwhelms the target’s resources and disrupts service.
Example: During a huge sale event, a group of hackers conducts a massive attack on an online retailer’s website. Many infected computers generate a massive load, rendering the site unreachable.
**Difference between DoS and DDoS Attacks:
The key difference between DoS and DDoS attacks lies in the number of sources used to flood the target. In a DoS attack, a single source is used to flood the target, while in a DDoS attack, multiple sources are coordinated to launch the attack. It’s like the difference between a single person trying to push down a door (DoS) and a crowd of people pushing together (DDoS).
Insider Threats
Insider threats involve malicious actions taken by individuals within an organisation, such as employees or contractors, who misuse their access to compromise security.
Example: A person who works for a company steals sensitive information and shares it with outsiders.
Social Engineering Attacks

Social engineering attacks manipulate human psychology to trick people into disclosing confidential information. This can include techniques like impersonation, pretexting, or baiting.
Example: Someone tricks you into disclosing private information or doing something illegal, like sharing passwords or clicking on harmful links.
Zero-day attacks
These are attacks that exploit vulnerabilities in software that the software vendor is not aware of. Zero-day attacks are often the most difficult to defend against because there is no patch available to fix the vulnerability.
Example: A hacker discovers a secret way to enter computer systems before anybody else does, giving them an advantage in causing damage.
What is the most common Cyber attack in Australia?
Phishing attacks continue to be the most popular and pervasive sort of cyber attack in Australia.
In 2022, there were over 2 million phishing attacks reported in the country, and these scams resulted in the loss of over $100 million.
As businesses and individuals try to stay vigilant against such threats, it’s important to note that even well-established technology providers have vulnerabilities that cybercriminals might exploit. For example, in August 2023, the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) highlighted important vulnerabilities in Microsoft’s security update. These vulnerabilities could potentially open doors for cyberattacks if left unpatched. Staying informed about such updates and implementing necessary fixes on time is a critical aspect of protecting against cyber threats in today’s digital landscape.
11 Effective Ways to Prevent Cyber Attacks

Employee Training
Educate your staff about the risks of cyberattacks, how to identify phishing attempts, and best practices for maintaining cybersecurity. Eventually businesses need to make sure that employees are aware of the different types of cyber attacks and how to protect themselves.
Strong Passwords
Passwords should be at least 12 characters long and include a mix of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Businesses should also require employees to change their passwords regularly.
Regular Updates
Keep all software, applications, and operating systems up to date to address vulnerabilities that cybercriminals may exploit. Software vendors often release security patches to fix vulnerabilities in their software. Businesses need to make sure that they install these security patches as soon as they are released.
Firewalls and Antivirus Software
Install and maintain robust firewall and antivirus solutions to protect against malware and unauthorized access. Moreover businesses should make sure that they have up-to-date security software installed on all of their computers.

Secure Wi-Fi Networks
Implement strong encryption and password protection for your Wi-Fi networks to prevent unauthorized access.
Data Encryption
Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest to ensure that even if it’s intercepted, it remains unintelligible to unauthorised users.
Access Control
Apply the principle of least privilege, granting users only the necessary permissions to minimize the risk of insider threats.
Backup plan
Perform regular data backups and store them securely offline to recover quickly in case of a business is hacked.

Incident Response Plan
Develop a comprehensive plan outlining the steps to take in the event of a cyber attack, minimising damage and downtime.
Be careful about what you click on
Phishing emails often contain links that, when clicked, will take the victim to a fake website. Businesses should train employees to be careful about what links they click on, and to only click on links that they know are legitimate.
Vendor Assessment
Assess the security practices of third-party vendors who have access to your systems or data, as their vulnerabilities can affect your business.
Certainly, by integrating these steps into your cybersecurity strategy, you can establish a resilient defense against cyber threats, aligning with the principles of the “Essential Eight” to improve your organisation’s cyber posture and provide a secure digital environment.

Undoubtedly, preventing cyberattacks requires a proactive approach that combines technological solutions with employee awareness and best practices. By understanding the types of cyber attacks, implementing robust security measures, and especially fostering a culture of cybersecurity within your company, you can considerably lower the chance of becoming a victim of cybercrime. Remember, cyber security is an ongoing effort that requires awareness, continuous learning, and the right tools to keep your business safe from the ever-changing threat of cyber attacks.
For expert guidance and tailored solutions to protect your business from cyber attacks, reach out to Netcomp Solutions, Australia’s leading IT services provider. Learn more about our cybersecurity products and other services by visiting our website.



