Boost your business with our advanced encryption solutions, ensuring top-notch security and confidentiality for your data


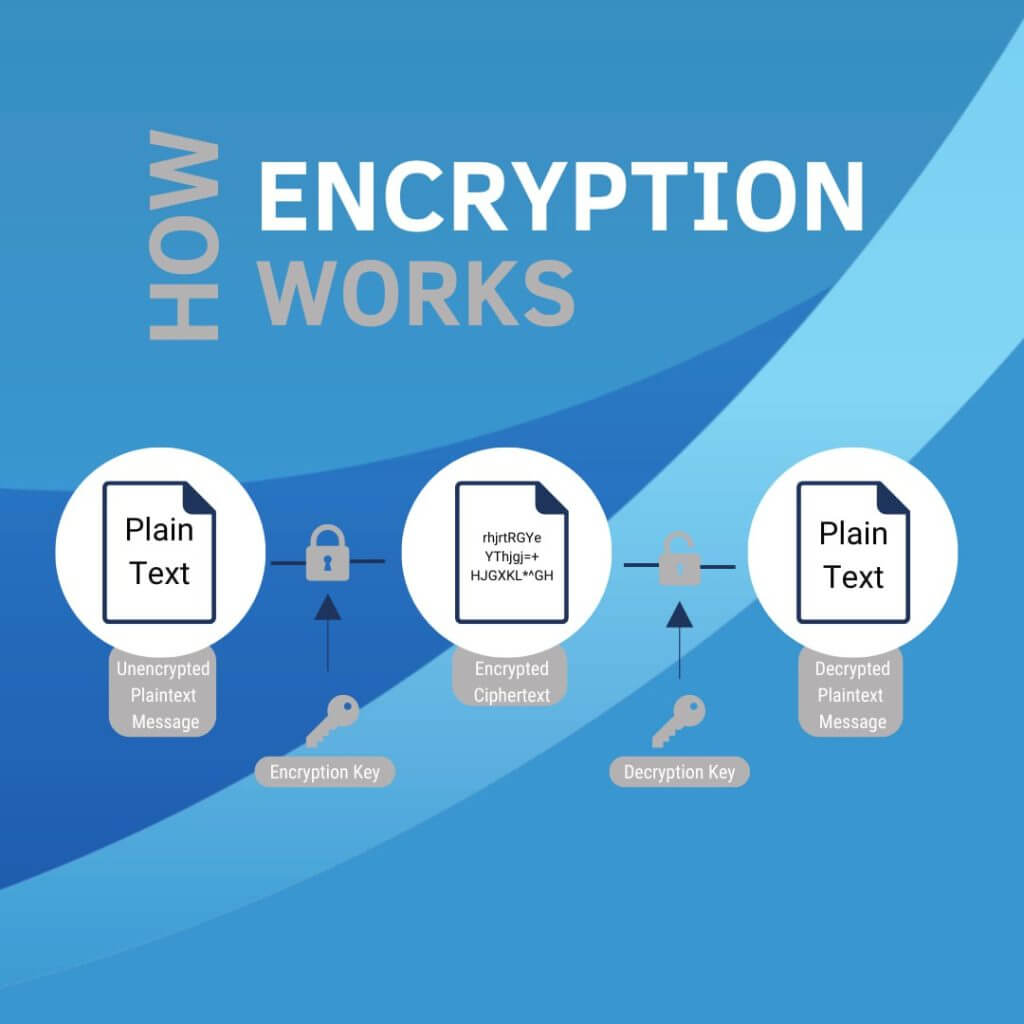
Data Encryption is a critical layer of cybersecurity that transforms readable data into a secure code, ensuring only those with the right key can access it.
This process, essential in the digital age, safeguards information from unauthorised access, making it a cornerstone for privacy and security across various sectors.
Data Encryption acts as a protective shield for sensitive information, guarding against data breaches and cyber threats.
It ensures confidentiality, maintains privacy, and aids in compliance with regulatory standards.
By encrypting data, organisations can protect their assets and foster trust among clients, emphasising the importance of robust data protection strategies in the modern cybersecurity landscape.
Encryption transforms readable data into a secure code, which can only be deciphered with a specific key.
It ensures that only authorised parties can access the information, safeguarding it from unauthorised access or theft.
This process is vital for protecting sensitive business data during transmission over the internet or while stored.


Ciphertext (means your sensitive business information transformed into a secure, unreadable format through encryption.
It’s the digital equivalent of a locked safe for your data, accessible only with the right key.
This encryption process shields your communications and stored information from unauthorised eyes, ensuring data privacy and protection against hacking.
Creating ciphertext typically requires the use of special software or tools that can encrypt plaintext.
This encryption software utilises algorithms to convert readable text into encrypted text (ciphertext), making it unreadable without the appropriate decryption key.
The specific software you might need depends on what you’re encrypting and the level of security you require.
Symmetric Encryption: Uses a single key for both encryption and decryption, ideal for large volumes of data.
Asymmetric Encryption: Employs a pair of keys, public and private, enhancing secure data exchange over unsecured channels.
Hash Functions: Converts data into a fixed-size string of characters, which is typically a one-way encryption without a key.
Tokenisation: Replaces sensitive data with unique identification symbols that retain all the essential information without compromising its security.
Data Protection: Keeps sensitive information safe from unauthorised access, ensuring privacy and confidentiality.
Regulatory Compliance: Helps businesses meet legal requirements for data security, avoiding penalties and fines.
Customer Trust: Enhances customer confidence by protecting their data, fostering trust and loyalty.
Risk Mitigation: Reduces the risk of data breaches and cyber threats, safeguarding business reputation and financial stability.
The current industry standard for data encryption is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). AES is widely recognised and used globally to protect sensitive data in transit and at rest.
It replaced the older Data Encryption Standard (DES) due to its stronger security features, including variable key lengths of 128, 192, and 256 bits.
AES is endorsed by the U.S. government and cybersecurity experts worldwide for its robustness against attacks and efficiency in various platforms and systems, making it the preferred choice for securing financial, personal, and national security information.
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and DES (Data Encryption Standard) are both symmetric key encryption algorithms, but AES is considered more secure and efficient than DES. DES, introduced in the 1970s, uses a 56-bit key that has become vulnerable to brute-force attacks due to advancements in computing power.
AES, adopted as an encryption standard in the early 2000s, offers key sizes of 128, 192, or 256 bits, providing a much higher level of security.
Its design to resist all known attacks, its speed, and flexibility in hardware and software environments have made AES the preferred encryption standard for governments, financial institutions, and other entities handling sensitive information.
While encrypted data significantly increases security, it is not entirely impervious to hackers.
However, without the correct decryption key, seeing the actual contents of encrypted data is extremely challenging for hackers.
Encryption transforms sensitive information into ciphertext, which is unreadable without the proper key.
While hackers might intercept encrypted data, deciphering it without the key is, for the most part, computationally impractical with current technology, especially with strong encryption standards like AES.
Nonetheless, vulnerabilities can exist, such as weak encryption algorithms or poorly managed encryption keys, which could potentially be exploited by determined attackers.
When we talk about the Data Encryption Standard (DES), we’re referring to a once widely-used method for encrypting electronic data.
Initially developed in the 1970s, DES was one of the first encryption algorithms that gained widespread adoption.
It uses a symmetric-key algorithm, meaning the same key is used for both encrypting and decrypting information.
The key size for DES is 56 bits, which was considered secure at the time of its creation.
For businesses, understanding encryption standards like DES is crucial for protecting sensitive information, ensuring that data like customer details, financial records, and proprietary information remains confidential and secure from unauthorised access.
For modern businesses in Australia, the original Data Encryption Standard (DES) is largely considered obsolete for protecting sensitive data.
This is primarily due to its 56-bit key size, which is no longer secure against brute-force attacks with today’s computing power.
In response to its vulnerabilities, DES was superseded by the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in the early 2000s.
AES offers significantly stronger security through larger key sizes (128, 192, and 256 bits), making it the preferred choice for businesses looking to safeguard their digital assets.
While DES might still be found in legacy systems, businesses are strongly advised to transition to more secure encryption methods like AES, in line with best practices and recommendations from cybersecurity authorities, to ensure robust protection against contemporary cyber threats.
Businesses looking to encrypt data need software that supports robust encryption standards like AES.
The choice of software depends on the specific needs, including encrypting data at rest (on storage devices), in transit (over networks), or both.
Solutions include full-disk encryption software like BitLocker for Windows or FileVault for macOS, email encryption tools that support PGP or S/MIME protocols, and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) for securing internet connections. Additionally, businesses handling large volumes of sensitive data might consider enterprise-level encryption solutions that offer centralised management and compliance features to meet regulatory requirements.
It’s crucial for businesses to select encryption software that aligns with their security needs and compliance obligations.
For businesses in Australia, the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a powerful tool for protecting data. Developed to replace the older, less secure DES, AES provides strong encryption through a symmetric key algorithm, using the same key for both encryption and decryption.
It’s available in various key sizes (128, 192, and 256 bits), with AES-256 offering the highest security level. AES is widely used across industries for protecting sensitive information, including online transactions, secure communications, and digital storage, making it a critical component of cybersecurity strategies for Australian businesses seeking to protect their digital assets efficiently.